Modern Logistics Powered by Plastic: The Industrial Shift Underway
The Transformation of Industrial Logistics Through Plastic Pallet Engineering
A Quiet Revolution in Supply Chains
Logistics, often described as the silent engine of commerce, is undergoing a metamorphosis. Hidden beneath container walls and conveyor belts lies a modest tool shaping this revolution: the pallet. Once an uncelebrated platform, it now stands at the epicenter of transformative engineering. The logistics industry is evolving—not with fanfare but with material mastery.
From Timber to Thermoplastics
Gone are the days when wood reigned supreme. The industry is now trading splinters for seamless polymeric platforms. The humble wooden pallet, while rugged and dependable, has ceded its dominance to plastic—sleeker, smarter, and significantly more strategic.
for more inform : https://market.us/report/plastic-pallet-market/
2. Historical Evolution of Industrial Pallets
The Wooden Workhorse Era
Since World War II, wooden pallets became the logistical backbone of global trade. Their charm lay in simplicity: easy to produce, easy to repair. But they also carried the burdens of splintering, susceptibility to moisture, and inconsistent sizing. Logistics managers tolerated inefficiencies as a cost of doing business.
Metal and Composite Interlude
As global trade grew in complexity, industries dabbled with metal and composite alternatives. Though offering strength, these iterations introduced their own dilemmas—weight, cost, and corrosion. It was clear: a new material had to rise—one both versatile and durable.
3. Rise of Plastic Pallet Engineering
The Science Behind the Shift
Plastic pallets are not mere substitutes; they are engineered evolutions. Behind each unit lies meticulous design rooted in thermodynamics, load distribution algorithms, and stress tolerance modeling. Engineers now treat pallets not as packaging tools, but as structural systems optimized for logistics.
Materials Innovation: From HDPE to Advanced Composites
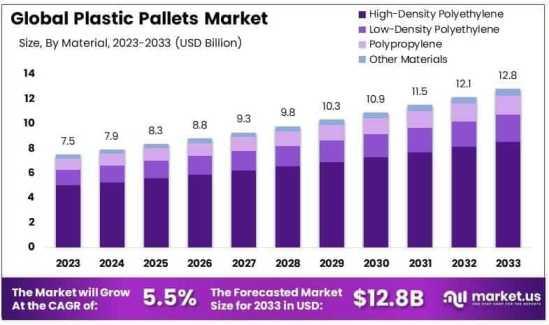
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) became the pioneer polymer, prized for its resilience and cost-effectiveness. But the future lies in composites—hybrids of glass fiber, recycled plastics, and bio-polymers. These materials offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, anti-microbial properties, and thermal resistance suited for the most demanding supply chains.
4. Impact on Industrial Logistics
Durability and Lifecycle Optimization
Plastic pallets can endure thousands of shipping cycles without degradation. Unlike wood, they resist water, mold, and pest infestation. This resilience drastically extends their operational life—cutting replacement costs and minimizing disruption.
Standardization and Automation Compatibility
In the age of robotic forklifts and automated storage retrieval systems (ASRS), uniformity is king. Plastic pallets provide exact dimensions, consistent weight distribution, and RFID embedding capability—making them perfect allies of warehouse automation and global standard compliance.
for more inform : https://market.us/report/plastic-pallet-market/
5. Environmental and Economic Dimensions
Reusability, Recyclability, and Carbon Footprint
A single plastic pallet can outlast 100 wooden ones, slashing waste in high-frequency logistics. Many are made from post-consumer plastic and are fully recyclable at end-of-life. This circular approach not only trims carbon emissions but also aligns with stringent ESG frameworks.
Cost Efficiency in the Long Run
Though upfront investment is higher, plastic pallets prove fiscally wise over time. Lower maintenance, fewer replacements, and improved load safety mean reduced total cost of ownership. They are not expenses—they're logistical assets.
6. Innovations Reshaping the Sector
IoT-Enabled Smart Pallets
Some plastic pallets now speak—embedded with sensors that monitor humidity, temperature, location, and shock. These smart pallets offer real-time insights, reducing spoilage in perishable goods transport and enhancing supply chain transparency.
Customization for Niche Industries
From pharmaceutical-grade sterilizable pallets to fire-retardant versions for aerospace cargo, customization is the new frontier. Plastic’s moldability allows engineering firms to tailor pallets with industry-specific capabilities, transforming them into purpose-built instruments rather than generic tools.
7. Challenges and the Road Ahead
Initial Capital Costs and Adoption Barriers
Despite the benefits, sticker shock remains a hurdle. Smaller enterprises hesitate, deterred by the upfront cost. However, leasing models and pay-per-use programs are emerging to democratize access and accelerate adoption.
The Future: Circular Economy and Modular Design
What lies ahead is even more revolutionary. Imagine pallets that disassemble for recycling, track carbon credits in real time, or adapt in shape for multi-format packaging. The integration of circular economy principles with modular design is poised to redefine the essence of what a pallet can be.
Plastic pallet engineering is not merely a trend—it’s a tectonic shift. As industries pursue efficiency, sustainability, and precision, these engineered platforms are lifting far more than goods. They are elevating the entire logistics paradigm.
The Transformation of Industrial Logistics Through Plastic Pallet Engineering
A Quiet Revolution in Supply Chains
Logistics, often described as the silent engine of commerce, is undergoing a metamorphosis. Hidden beneath container walls and conveyor belts lies a modest tool shaping this revolution: the pallet. Once an uncelebrated platform, it now stands at the epicenter of transformative engineering. The logistics industry is evolving—not with fanfare but with material mastery.
From Timber to Thermoplastics
Gone are the days when wood reigned supreme. The industry is now trading splinters for seamless polymeric platforms. The humble wooden pallet, while rugged and dependable, has ceded its dominance to plastic—sleeker, smarter, and significantly more strategic.
for more inform : https://market.us/report/plastic-pallet-market/
2. Historical Evolution of Industrial Pallets
The Wooden Workhorse Era
Since World War II, wooden pallets became the logistical backbone of global trade. Their charm lay in simplicity: easy to produce, easy to repair. But they also carried the burdens of splintering, susceptibility to moisture, and inconsistent sizing. Logistics managers tolerated inefficiencies as a cost of doing business.
Metal and Composite Interlude
As global trade grew in complexity, industries dabbled with metal and composite alternatives. Though offering strength, these iterations introduced their own dilemmas—weight, cost, and corrosion. It was clear: a new material had to rise—one both versatile and durable.
3. Rise of Plastic Pallet Engineering
The Science Behind the Shift
Plastic pallets are not mere substitutes; they are engineered evolutions. Behind each unit lies meticulous design rooted in thermodynamics, load distribution algorithms, and stress tolerance modeling. Engineers now treat pallets not as packaging tools, but as structural systems optimized for logistics.
Materials Innovation: From HDPE to Advanced Composites
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) became the pioneer polymer, prized for its resilience and cost-effectiveness. But the future lies in composites—hybrids of glass fiber, recycled plastics, and bio-polymers. These materials offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, anti-microbial properties, and thermal resistance suited for the most demanding supply chains.
4. Impact on Industrial Logistics
Durability and Lifecycle Optimization
Plastic pallets can endure thousands of shipping cycles without degradation. Unlike wood, they resist water, mold, and pest infestation. This resilience drastically extends their operational life—cutting replacement costs and minimizing disruption.
Standardization and Automation Compatibility
In the age of robotic forklifts and automated storage retrieval systems (ASRS), uniformity is king. Plastic pallets provide exact dimensions, consistent weight distribution, and RFID embedding capability—making them perfect allies of warehouse automation and global standard compliance.
for more inform : https://market.us/report/plastic-pallet-market/
5. Environmental and Economic Dimensions
Reusability, Recyclability, and Carbon Footprint
A single plastic pallet can outlast 100 wooden ones, slashing waste in high-frequency logistics. Many are made from post-consumer plastic and are fully recyclable at end-of-life. This circular approach not only trims carbon emissions but also aligns with stringent ESG frameworks.
Cost Efficiency in the Long Run
Though upfront investment is higher, plastic pallets prove fiscally wise over time. Lower maintenance, fewer replacements, and improved load safety mean reduced total cost of ownership. They are not expenses—they're logistical assets.
6. Innovations Reshaping the Sector
IoT-Enabled Smart Pallets
Some plastic pallets now speak—embedded with sensors that monitor humidity, temperature, location, and shock. These smart pallets offer real-time insights, reducing spoilage in perishable goods transport and enhancing supply chain transparency.
Customization for Niche Industries
From pharmaceutical-grade sterilizable pallets to fire-retardant versions for aerospace cargo, customization is the new frontier. Plastic’s moldability allows engineering firms to tailor pallets with industry-specific capabilities, transforming them into purpose-built instruments rather than generic tools.
7. Challenges and the Road Ahead
Initial Capital Costs and Adoption Barriers
Despite the benefits, sticker shock remains a hurdle. Smaller enterprises hesitate, deterred by the upfront cost. However, leasing models and pay-per-use programs are emerging to democratize access and accelerate adoption.
The Future: Circular Economy and Modular Design
What lies ahead is even more revolutionary. Imagine pallets that disassemble for recycling, track carbon credits in real time, or adapt in shape for multi-format packaging. The integration of circular economy principles with modular design is poised to redefine the essence of what a pallet can be.
Plastic pallet engineering is not merely a trend—it’s a tectonic shift. As industries pursue efficiency, sustainability, and precision, these engineered platforms are lifting far more than goods. They are elevating the entire logistics paradigm.
Modern Logistics Powered by Plastic: The Industrial Shift Underway
The Transformation of Industrial Logistics Through Plastic Pallet Engineering
A Quiet Revolution in Supply Chains
Logistics, often described as the silent engine of commerce, is undergoing a metamorphosis. Hidden beneath container walls and conveyor belts lies a modest tool shaping this revolution: the pallet. Once an uncelebrated platform, it now stands at the epicenter of transformative engineering. The logistics industry is evolving—not with fanfare but with material mastery.
From Timber to Thermoplastics
Gone are the days when wood reigned supreme. The industry is now trading splinters for seamless polymeric platforms. The humble wooden pallet, while rugged and dependable, has ceded its dominance to plastic—sleeker, smarter, and significantly more strategic.
for more inform : https://market.us/report/plastic-pallet-market/
2. Historical Evolution of Industrial Pallets
The Wooden Workhorse Era
Since World War II, wooden pallets became the logistical backbone of global trade. Their charm lay in simplicity: easy to produce, easy to repair. But they also carried the burdens of splintering, susceptibility to moisture, and inconsistent sizing. Logistics managers tolerated inefficiencies as a cost of doing business.
Metal and Composite Interlude
As global trade grew in complexity, industries dabbled with metal and composite alternatives. Though offering strength, these iterations introduced their own dilemmas—weight, cost, and corrosion. It was clear: a new material had to rise—one both versatile and durable.
3. Rise of Plastic Pallet Engineering
The Science Behind the Shift
Plastic pallets are not mere substitutes; they are engineered evolutions. Behind each unit lies meticulous design rooted in thermodynamics, load distribution algorithms, and stress tolerance modeling. Engineers now treat pallets not as packaging tools, but as structural systems optimized for logistics.
Materials Innovation: From HDPE to Advanced Composites
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) became the pioneer polymer, prized for its resilience and cost-effectiveness. But the future lies in composites—hybrids of glass fiber, recycled plastics, and bio-polymers. These materials offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, anti-microbial properties, and thermal resistance suited for the most demanding supply chains.
4. Impact on Industrial Logistics
Durability and Lifecycle Optimization
Plastic pallets can endure thousands of shipping cycles without degradation. Unlike wood, they resist water, mold, and pest infestation. This resilience drastically extends their operational life—cutting replacement costs and minimizing disruption.
Standardization and Automation Compatibility
In the age of robotic forklifts and automated storage retrieval systems (ASRS), uniformity is king. Plastic pallets provide exact dimensions, consistent weight distribution, and RFID embedding capability—making them perfect allies of warehouse automation and global standard compliance.
for more inform : https://market.us/report/plastic-pallet-market/
5. Environmental and Economic Dimensions
Reusability, Recyclability, and Carbon Footprint
A single plastic pallet can outlast 100 wooden ones, slashing waste in high-frequency logistics. Many are made from post-consumer plastic and are fully recyclable at end-of-life. This circular approach not only trims carbon emissions but also aligns with stringent ESG frameworks.
Cost Efficiency in the Long Run
Though upfront investment is higher, plastic pallets prove fiscally wise over time. Lower maintenance, fewer replacements, and improved load safety mean reduced total cost of ownership. They are not expenses—they're logistical assets.
6. Innovations Reshaping the Sector
IoT-Enabled Smart Pallets
Some plastic pallets now speak—embedded with sensors that monitor humidity, temperature, location, and shock. These smart pallets offer real-time insights, reducing spoilage in perishable goods transport and enhancing supply chain transparency.
Customization for Niche Industries
From pharmaceutical-grade sterilizable pallets to fire-retardant versions for aerospace cargo, customization is the new frontier. Plastic’s moldability allows engineering firms to tailor pallets with industry-specific capabilities, transforming them into purpose-built instruments rather than generic tools.
7. Challenges and the Road Ahead
Initial Capital Costs and Adoption Barriers
Despite the benefits, sticker shock remains a hurdle. Smaller enterprises hesitate, deterred by the upfront cost. However, leasing models and pay-per-use programs are emerging to democratize access and accelerate adoption.
The Future: Circular Economy and Modular Design
What lies ahead is even more revolutionary. Imagine pallets that disassemble for recycling, track carbon credits in real time, or adapt in shape for multi-format packaging. The integration of circular economy principles with modular design is poised to redefine the essence of what a pallet can be.
Plastic pallet engineering is not merely a trend—it’s a tectonic shift. As industries pursue efficiency, sustainability, and precision, these engineered platforms are lifting far more than goods. They are elevating the entire logistics paradigm.
0 Comments
0 Shares
1K Views
0 Reviews