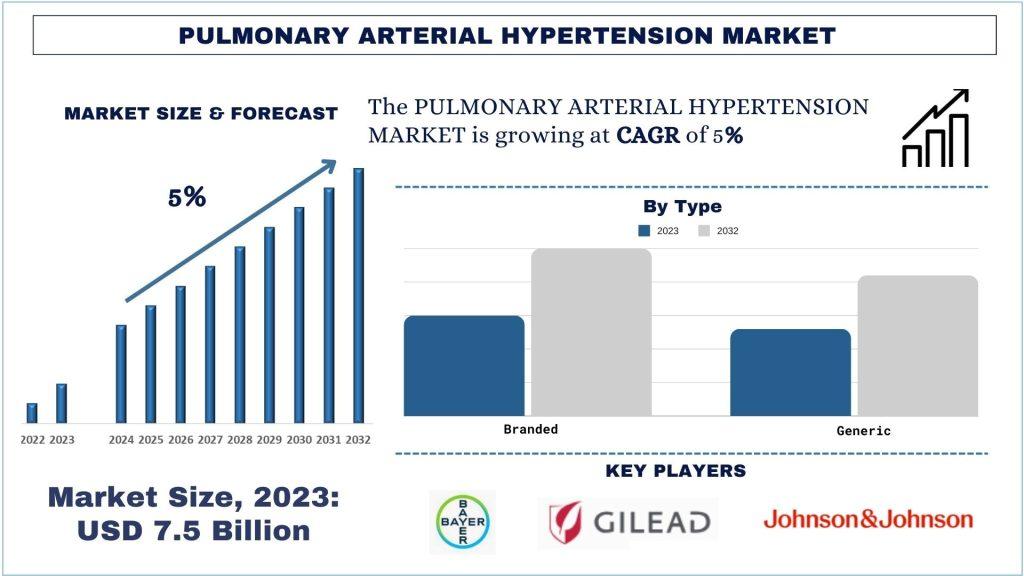
According to the UnivDatos Market Insights analysis, the surge in the incidence of PAH cases and the rise in demand for personalized medicine will drive the global scenario of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. As per their “Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Market” report, the global market was valued at USD 7.5 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of about 5% during the forecast period from 2024 – 2032.
The Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension market in North America has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by various factors such as the increasing incidence of PAH, supplemented by a rising geriatric population, rising adoption of innovative therapies, and rising awareness about personalized medicine, etc. North America, particularly the U.S., represents one of the largest markets for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension globally. The market encompasses a wide range of applications to improve the PAH. Here's a detailed overview:
Driving Factors for the Market in North America:
One major factor propelling the Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) market in North America is the rising incidence of these chronic inflammatory conditions. For instance, as per the data of American Heart Association (AHA) 2021, the prevalence of PAH in the United States is estimated to be between 15 and 50 cases per million people, with an incidence of about 2-5 cases per million adults annually. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) is a chronic and progressive disease characterized by high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, which supply blood from the heart to the lungs. This condition results in the narrowing and stiffening of these arteries, making it difficult for blood to flow through the lungs and increasing the workload on the right side of the heart. If left untreated, PAH can lead to right heart failure and other serious complications. The North American PAH market includes a variety of therapeutic options, including endothelin receptor antagonists, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, prostacyclin analogs, soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators, and calcium channel blockers. The market is driven by advancements in medical research, increasing awareness, and supportive healthcare policies.
In recent years, there has been a notable increase in the incidence and prevalence of PAH across North America. This trend is attributed to several factors:
1. Improved Diagnostic Techniques:
Advances in diagnostic technologies, such as echocardiography, right heart catheterization, and high-resolution imaging techniques, have led to earlier and more accurate detection of PAH. This has contributed to a higher reported prevalence as more cases are identified and diagnosed.
2. Aging Population:
The aging population in North America is a significant factor contributing to the increasing prevalence of PAH. Older adults are at a higher risk for developing PAH due to age-related changes in the cardiovascular system and the higher likelihood of comorbid conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and heart disease.
3. Increased Awareness and Screening:
Greater awareness of PAH among healthcare providers and the public has led to more widespread screening and early diagnosis. Education campaigns and professional training programs have emphasized the importance of recognizing PAH symptoms early, leading to a rise in diagnosed cases.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=61552
4. Higher Survival Rates:
Advances in PAH treatments and patient management strategies have improved survival rates, resulting in a growing population of individuals living with PAH. As treatments become more effective at managing symptoms and slowing disease progression, more patients are being maintained on long-term therapy.
5. Increased Incidence of Associated Conditions:
The rising incidence of conditions associated with PAH, such as connective tissue diseases (e.g., systemic sclerosis), HIV, and congenital heart disease, has also contributed to the growing prevalence of PAH. These comorbid conditions are known risk factors for developing PAH and are becoming more commonly diagnosed and managed.
6. Genetic and Environmental Factors:
Ongoing research has identified genetic predispositions and environmental factors that may contribute to the development of PAH. Familial PAH cases, linked to specific gene mutations, and exposure to environmental toxins or drugs have been shown to increase the risk of PAH, leading to more cases being reported.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the increasing prevalence of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in North America can be attributed to a combination of improved diagnostic capabilities, an aging population, heightened awareness and screening efforts, better survival rates due to advanced treatments, and the rising incidence of associated conditions. These factors collectively contribute to a growing number of PAH cases, underscoring the need for continued research, innovation, and healthcare resources to effectively manage and treat this complex condition.
Contact Us:
UnivDatos Market Insights
Email - contact@univdatos.com
Contact Number - +1 9782263411
Website -www.univdatos.com