Horizontal oil drilling stands as a pioneering innovation within the oil and gas industry, revolutionizing the accessibiHorizontal Oil Drillinglity and production of hydrocarbon resources. In this exploration, we delve into the intricacies of horizontal oil drilling, its associated advantages, challenges, environmental considerations, and the indispensable role played by simulation technology in this transformative process.
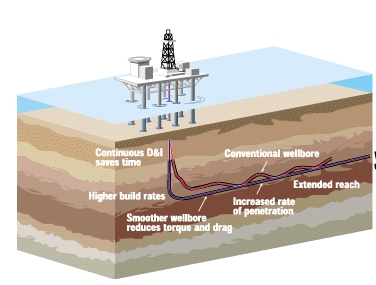
The Process of Horizontal Oil Drilling
Horizontal drilling, also known as directional drilling, involves drilling a wellbore at an angle to access oil or gas reservoirs beneath the Earth's surface. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Vertical Drilling: Initially, a wellbore is drilled vertically from the surface to a certain depth.
Build Section: At a specified depth, the drilling direction is altered, curving the wellbore to create a "build section."
Horizontal Drilling: Following the curve, the wellbore extends horizontally through the oil or gas reservoir.
Well Completion: Once the desired horizontal length is achieved, the well is completed with casing and cement to facilitate production.
Advantages of Horizontal Oil Drilling
Increased Reservoir Access: Horizontal drilling allows access to previously inaccessible reserves, enhancing the amount of recoverable oil and gas.
Enhanced Recovery Rates: The horizontal portion of a well provides increased contact with the reservoir, leading to higher recovery rates.
Reduced Environmental Impact: Operators can minimize surface footprint and environmental damage by accessing reservoirs from a single drilling location.
Improved Well Economics: Horizontal drilling offers commercial appeal with higher recovery rates and lower drilling costs.
Enhanced Well Control: By controlling the trajectory, operators can avoid geological complications and drilling issues.

Challenges and Environmental Considerations
Challenges:
Technical Complexity: Horizontal drilling requires sophisticated equipment and expertise, making it more technically demanding than vertical drilling.
Increased Costs: The technology and expertise involved in horizontal drilling may lead to higher initial expenses.
Regulatory Compliance: Strict adherence to regulations is crucial for safe and environmentally responsible drilling.
Wellbore Integrity: Maintaining wellbore integrity is essential to prevent accidents and ensure long-term productivity.
Environmental Considerations:
Reduced Surface Impact: Horizontal drilling minimizes surface disruption, particularly beneficial in ecologically sensitive areas.
Risk of Contamination: Careful management is required to prevent groundwater contamination from drilling fluids and hydrocarbon migration.
Spill Prevention: Comprehensive spill prevention plans are essential to address environmental risks effectively.
Habitat Protection: Operators must consider the impact on local wildlife habitats and ecosystems.
The Vital Role of Simulation Technology
Simulation technology plays a crucial role in optimizing horizontal drilling operations:

Geosteering: Drilling simulators utilizes 3D models of the subsurface to guide the drill bit precisely within the reservoir in real-time.
Drilling Trajectory Planning: Designs the ideal well path, considering geological data, wellbore stability, and reservoir parameters.
Wellbore Stability Analysis: Predicts mechanical behavior, evaluates strains and pressures, and forecasts potential issues like wellbore collapse or fluid ingress.
Real-time Monitoring and Adjustments: Provides immediate feedback for drillers to make adjustments to drilling parameters during the operation.
Benefits of Simulation in Horizontal Drilling
Precision and Accuracy: Simulation ensures precise wellbore placement, minimizing deviation and intercepting the most productive reservoir areas.
Enhanced Efficiency: Optimizes trajectories and parameters, reducing drilling time, operational costs, and complications.
Risk Mitigation: Identifies potential challenges in advance, enabling proactive risk management and stability assurance.
Improved Recovery Rates: Accurate placement maximizes recovery, leading to higher production rates and profitability.
Safety and Environmental Protection: Virtual emergency simulation Prevents safety risks and environmental concerns by avoiding issues like instability and fluid influx.
Conclusion
Horizontal oil drilling has reshaped the oil and gas industry, unlocking previously inaccessible resources and increasing recovery rates. Simulation technology ensures that drilling operations are optimized for maximum recovery and safety. As the industry continues to evolve, horizontal drilling will play a pivotal role in meeting energy demands sustainably while safeguarding the environment.


