As the global demand for lithium-ion batteries continues to surge, driven by advancements in electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage, the future of lithium-ion battery recycling is poised for transformative changes. Trends and innovations in this sector are setting the stage for more efficient, sustainable, and economically viable recycling practices.
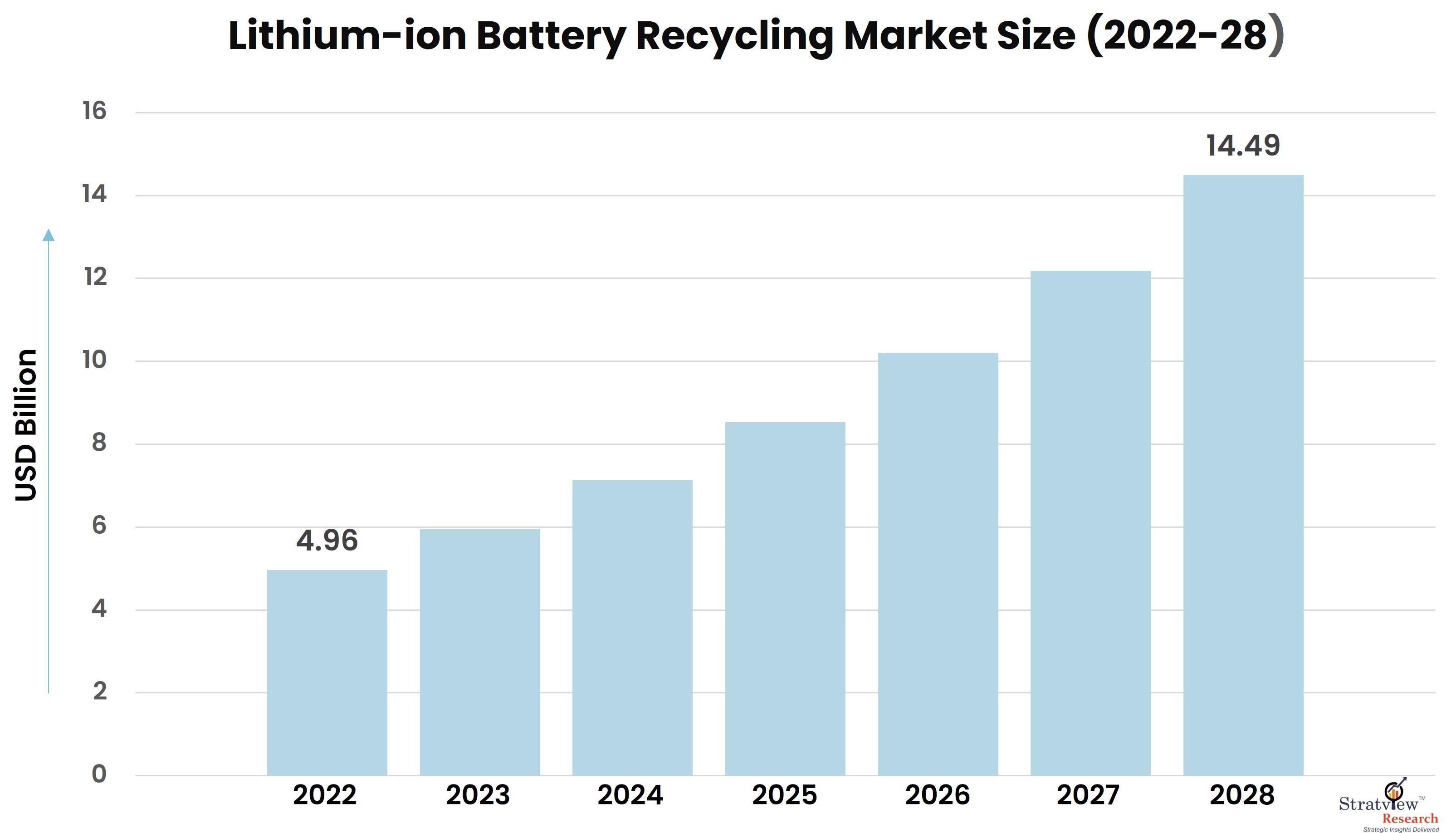
According to Stratview Research, the lithium-ion battery recycling market was estimated at USD 4.96 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 19.48% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 14.49 billion in 2028.
Trends Shaping the Future
Advanced Recycling Technologies: The development of advanced recycling technologies is a major trend in the lithium-ion battery recycling industry. Traditional recycling methods, such as pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical processes, are being enhanced by innovations like direct recycling. Direct recycling techniques, which aim to preserve the battery's structural integrity, can potentially reduce energy consumption and improve the quality of recycled materials.
Circular Economy Integration: The circular economy model, emphasizing the reuse and recycling of materials to minimize waste, is increasingly influencing the battery recycling industry. Companies are focusing on designing batteries with recyclability in mind, integrating more easily recyclable materials, and establishing closed-loop systems that ensure that end-of-life batteries are efficiently recovered and reprocessed.
Increased Automation: Automation is revolutionizing battery recycling by improving efficiency and reducing labor costs. Advanced robotic systems and automated sorting technologies are streamlining the disassembly and processing of batteries, enhancing both safety and productivity in recycling facilities.
Regulatory and Policy Developments: Governments are increasingly implementing stricter regulations and incentives to support battery recycling. Policies that mandate recycling targets, provide financial incentives for recycling infrastructure, and promote research into sustainable recycling methods are driving industry advancements and encouraging investment.
Innovations on the Horizon
Improved Material Recovery: Innovations in material recovery processes are focusing on extracting high-purity metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel from used batteries. Techniques such as bioleaching and novel chemical processes are being explored to enhance the efficiency and yield of material recovery, making the recycling process more economically viable.
Second-Life Applications: Beyond recycling, there is growing interest in repurposing used batteries for second-life applications. Used lithium-ion batteries, particularly those from EVs, can be refurbished and repurposed for energy storage systems in homes and businesses, extending their lifecycle and providing valuable grid stability solutions.
Enhanced Battery Design: Future battery designs are likely to incorporate materials and structures that facilitate easier recycling. Researchers are exploring the use of more recyclable components, modular designs that simplify disassembly, and materials that are less toxic and more abundant.
Global Collaboration: As the demand for lithium-ion batteries grows, global collaboration among manufacturers, recyclers, and policymakers is becoming crucial. Collaborative efforts are focusing on standardizing recycling practices, sharing best practices, and developing international frameworks to address the challenges of battery recycling on a global scale.
In summary, the future of lithium-ion battery recycling is marked by significant trends and innovations aimed at improving efficiency, sustainability, and economic viability. As technological advancements and regulatory frameworks evolve, the industry is set to play a crucial role in supporting the transition to a more sustainable energy future.