How to Manage Swelling of Deeper Skin Layers?
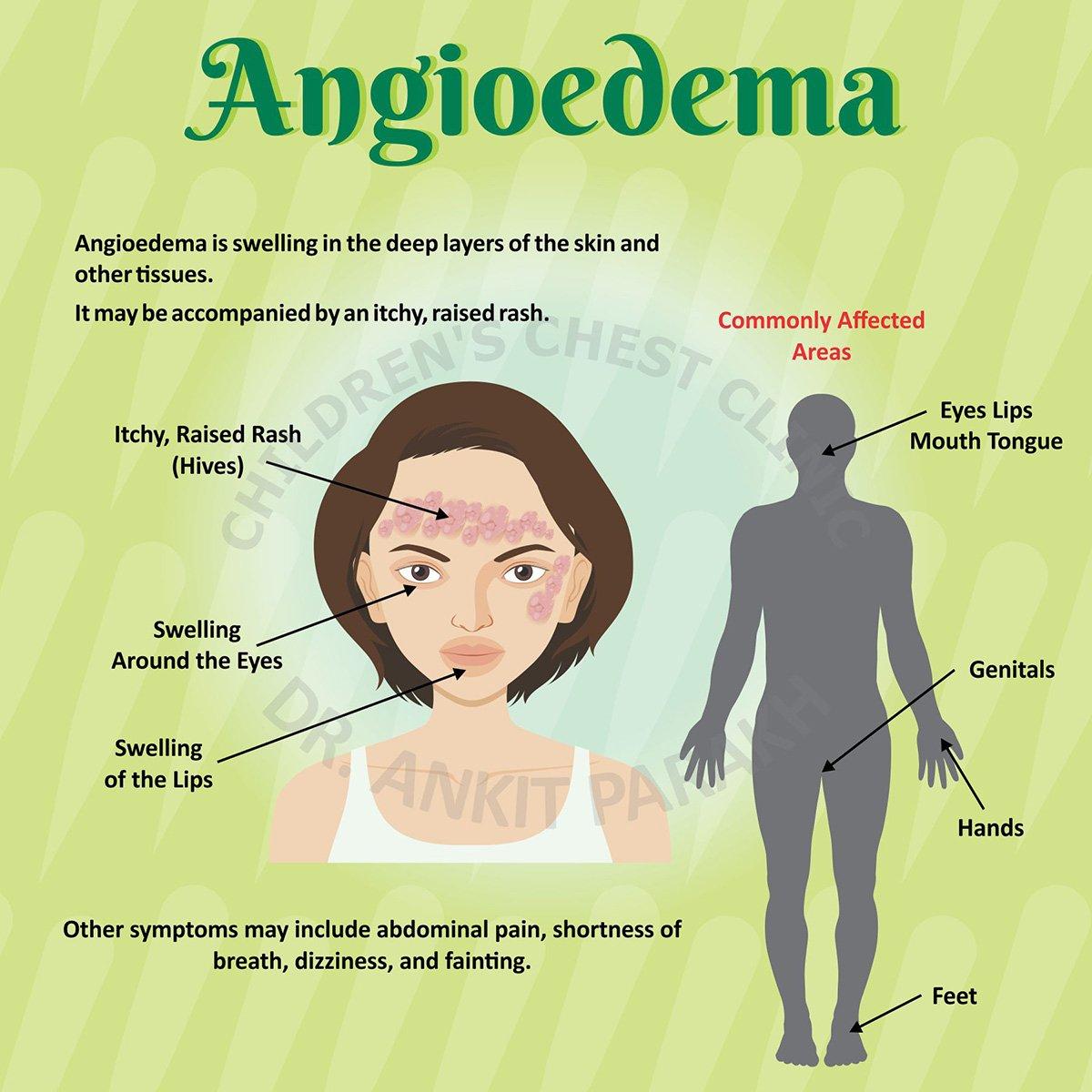
Swelling of the deeper skin layers, often referred to as angioedema or deep tissue edema, is a condition characterized by fluid accumulation in the subcutaneous tissues or deeper dermal layers. This can result from various causes, including infections, allergic reactions, trauma, or underlying medical conditions. Effective management requires a clear understanding of the underlying cause, timely intervention, and appropriate treatment strategies. This article provides a detailed guide on managing swelling in the deeper skin layers, incorporating insights on the role of antibiotics like ceftriaxone, a widely used medication from trusted ceftriaxone supplier sources, in treating infection-related swelling.
Understanding Swelling of Deeper Skin Layers
Swelling in the deeper skin layers differs from superficial swelling, as it affects tissues beneath the epidermis, including the dermis, subcutaneous fat, and sometimes underlying muscles. Common causes include:
-
Infections: Bacterial infections like cellulitis or abscesses can lead to deep tissue swelling. These often require antibiotics from a reliable ceftriaxone supplier to address the infection effectively.
-
Allergic Reactions: Angioedema, often triggered by allergens, medications, or hereditary factors, causes rapid swelling in deeper tissues.
-
Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma can lead to fluid accumulation in deeper layers, resulting in swelling.
-
Medical Conditions: Conditions like lymphedema, venous insufficiency, or autoimmune disorders can cause chronic swelling.
-
Medications: Certain drugs, including ACE inhibitors, can induce angioedema as a side effect.
Symptoms may include localized or diffuse swelling, pain, redness, warmth, or systemic signs like fever in cases of infection. Severe cases may impair mobility or cause complications if untreated.
Step-by-Step Management of Deep Skin Swelling
1. Identify the Underlying Cause
The first step in managing swelling is determining its cause. A healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination, review medical history, and may order diagnostic tests such as blood work, imaging (ultrasound, CT scan), or skin biopsies. For infection-related swelling, identifying the causative organism is critical, as this guides antibiotic selection. Ceftriaxone, sourced from a reputable ceftriaxone supplier, is often prescribed for bacterial infections like cellulitis or abscesses due to its broad-spectrum efficacy.
2. Address Infection Promptly
If the swelling is due to a bacterial infection, prompt antibiotic therapy is essential. Ceftriaxone, a third-generation cephalosporin, is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species, commonly implicated in skin infections. Administered intravenously or intramuscularly, ceftriaxone targets deep tissue infections effectively. Ensure the medication is obtained from a trusted ceftriaxone supplier to guarantee quality and efficacy. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for intravenous administration and monitoring.
3. Manage Allergic Reactions
For angioedema caused by allergic reactions, immediate cessation of the triggering agent (e.g., a medication or food) is crucial. Antihistamines, corticosteroids, or epinephrine may be prescribed in acute cases. For hereditary angioedema, specific treatments like C1 esterase inhibitors may be necessary. Unlike infections, allergic swelling typically does not require antibiotics like ceftriaxone unless a secondary infection develops.
4. Reduce Inflammation
Anti-inflammatory medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids, can help reduce swelling and pain in non-infectious cases. For example, ibuprofen or prednisone may be prescribed to manage inflammation caused by trauma or autoimmune conditions. However, these should be used cautiously and under medical supervision to avoid side effects.
5. Elevate and Compress Affected Areas
Physical measures like elevation and compression can reduce swelling by promoting fluid drainage. Elevating the affected limb above heart level helps reduce fluid accumulation in cases of lymphedema or venous insufficiency. Compression garments or bandages, when applied correctly, can prevent further fluid buildup. Ensure compression is not too tight, as it may impair circulation.
6. Drain Fluid if Necessary
In cases of abscesses or large fluid collections, surgical drainage may be required. This procedure, performed under sterile conditions, removes pus or excess fluid, alleviating pressure and swelling. Post-drainage, antibiotics like ceftriaxone from a reliable ceftriaxone supplier are often prescribed to prevent recurrence or treat residual infection.
7. Treat Underlying Conditions
Chronic conditions like lymphedema or venous insufficiency require long-term management. Lymphatic drainage massage, compression therapy, or lifestyle changes (e.g., weight management, exercise) can help. For autoimmune-related swelling, immunosuppressive therapies may be needed. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment.
8. Supportive Care
Supportive measures, such as hydration, pain management, and wound care, are vital. Keeping the skin clean and moisturized prevents secondary infections, especially in cases of recurrent swelling. Nutritional support, including a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids), can aid recovery.
Role of Ceftriaxone in Managing Infection-Related Swelling
Ceftriaxone is a cornerstone in treating bacterial infections causing deep skin swelling, such as cellulitis, erysipelas, or abscesses. Its broad-spectrum activity covers gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, making it a versatile choice. Sourced from a reputable ceftriaxone supplier, it ensures consistent potency and safety. Key points about ceftriaxone use include:
-
Administration: Typically given as an intravenous or intramuscular injection, with dosing based on infection severity and patient factors (e.g., age, kidney function).
-
Duration: Treatment usually lasts 7–14 days, depending on the infection’s resolution. Prolonged use should be avoided to minimize resistance.
-
Monitoring: Regular monitoring for side effects, such as allergic reactions or gastrointestinal issues, is necessary. Blood tests may be required to assess liver or kidney function during prolonged therapy.
-
Resistance Concerns: Overuse of antibiotics can lead to resistance, so ceftriaxone should only be used when indicated, with confirmation of bacterial infection.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting ceftriaxone, and ensure the medication is sourced from a certified ceftriaxone supplier to avoid counterfeit or substandard products.
Preventive Measures
Preventing recurrence of deep skin swelling involves addressing risk factors and maintaining overall health:
-
Skin Hygiene: Keep the skin clean and dry to prevent infections. Use mild soaps and moisturizers to maintain skin integrity.
-
Injury Prevention: Protect skin from trauma or cuts, which can serve as entry points for bacteria.
-
Allergy Management: Identify and avoid allergens. Carry an epinephrine auto-injector if prone to severe allergic reactions.
-
Chronic Condition Management: Follow treatment plans for conditions like diabetes, lymphedema, or venous insufficiency to minimize swelling risk.
-
Regular Checkups: Routine medical evaluations can detect early signs of swelling or related complications.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Immediate medical attention is warranted if swelling is accompanied by:
-
Severe pain or rapid worsening
-
High fever or chills
-
Difficulty breathing or swallowing (common in angioedema)
-
Signs of systemic infection (e.g., confusion, rapid heart rate)
-
Persistent swelling despite treatment
Early intervention can prevent complications, such as sepsis in infection cases or airway obstruction in angioedema.
Conclusion
Managing swelling of the deeper skin layers requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the underlying cause. Infections, a common culprit, are effectively treated with antibiotics like ceftriaxone from a trusted ceftriaxone supplier. Other strategies, including anti-inflammatory medications, elevation, compression, and surgical drainage, play critical roles depending on the etiology. Preventive measures and timely medical consultation are key to avoiding recurrence and complications. By understanding the cause and applying targeted interventions, individuals can effectively manage and resolve deep skin swelling, improving quality of life and preventing long-term issues.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


