Hydrogel-based Drug Delivery Market Impacting Factors: Drivers and Barriers to Systemic Adoption
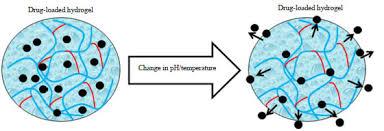
The hydrogel-based drug delivery market is increasingly recognized as a key area of growth within the pharmaceutical and biomedical industries. A closer look at the market reveals a complex interplay of factors that shape its current trajectory and future prospects. From advancements in material science and rising chronic disease prevalence to regulatory challenges and economic considerations, several critical elements are actively influencing the development, commercialization, and adoption of hydrogel-based drug delivery systems.
One of the most prominent factors impacting the market is the rising demand for targeted and controlled drug delivery mechanisms. With an aging global population and an increasing burden of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders, there is growing pressure on healthcare systems to adopt delivery solutions that are not only more effective but also less invasive and better tolerated by patients. Hydrogel-based systems address this need by enabling localized, sustained, and stimuli-responsive drug release, minimizing systemic exposure and improving therapeutic outcomes. Their unique ability to encapsulate and protect sensitive drugs—such as proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids—further amplifies their relevance in advanced treatment paradigms.
Technological innovation is another key influencing factor. Research into novel hydrogel formulations—especially smart hydrogels that respond to pH, temperature, or enzymes—is driving the creation of highly tailored drug delivery systems. The integration of hydrogels with nanotechnology, microfluidics, and bioelectronics is expanding their functional scope, leading to applications in wearable devices and regenerative medicine. These innovations are not only pushing the boundaries of therapeutic possibilities but are also fostering competitive differentiation among developers. The rapid pace of innovation, however, also requires continuous investment in research and clinical validation, which may pose a barrier for smaller players.
Regulatory considerations significantly impact the hydrogel-based drug delivery market, particularly for products that are classified as combination devices. The dual regulatory pathways for devices and pharmaceuticals often lead to extended approval timelines, complex compliance requirements, and additional testing phases. This can delay market entry and increase development costs. Moreover, the lack of clear guidelines in some regions for evaluating the performance and safety of hydrogel-based systems can deter investment and slow the pace of innovation. Regulatory harmonization and clearer approval frameworks are essential for accelerating the translation of research into clinical practice.
Manufacturing scalability and quality control are also vital impacting factors. While hydrogels offer versatile design parameters, their production at scale presents challenges in terms of consistency, sterility, and stability. Ensuring uniform drug distribution, maintaining mechanical integrity, and managing storage conditions are critical to product success. Manufacturers must invest in advanced production techniques, including 3D printing and automated gelation systems, to ensure reliable and cost-effective outputs. Failure to meet quality standards can result in recalls, reputational damage, and financial losses, making manufacturing efficiency a key determinant of market competitiveness.
Economic and reimbursement dynamics further shape the commercial viability of hydrogel-based drug delivery systems. The high initial development costs and relatively limited reimbursement pathways in some healthcare systems can restrict adoption. Payers often require substantial evidence of clinical efficacy and cost-effectiveness before approving coverage, particularly for novel or premium-priced delivery platforms. Companies must navigate these economic pressures by investing in health economics studies and engaging with stakeholders early in the development process to build the necessary case for value-based adoption.
Intellectual property (IP) protection is another crucial element influencing market behavior. The ability to secure patents for novel hydrogel compositions, drug-loading techniques, and delivery mechanisms plays a central role in attracting investment and establishing market exclusivity. Firms that build robust IP portfolios are better positioned to license their technologies, enter strategic partnerships, or pursue acquisitions. Conversely, weak or contested patents can lead to litigation, erode competitive advantages, and discourage innovation.
Finally, patient and provider awareness significantly affect the uptake of hydrogel-based drug delivery systems. Healthcare professionals may be cautious in adopting new delivery platforms without sufficient clinical familiarity or training. Similarly, patients may have concerns about novel administration routes or product formats. Education initiatives, clinical trials, and real-world evidence generation are essential to overcoming these psychological and practical barriers to adoption.
In conclusion, the hydrogel-based drug delivery market is influenced by a dynamic set of factors encompassing clinical demand, technological advancement, regulatory complexity, economic feasibility, and stakeholder perception. Addressing these impacting elements holistically will be critical to accelerating market growth and fully realizing the therapeutic potential of hydrogel technologies in diverse medical fields.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


