High-Power Rectifiers Market Challenges: Overcoming Barriers in High-Voltage Innovation
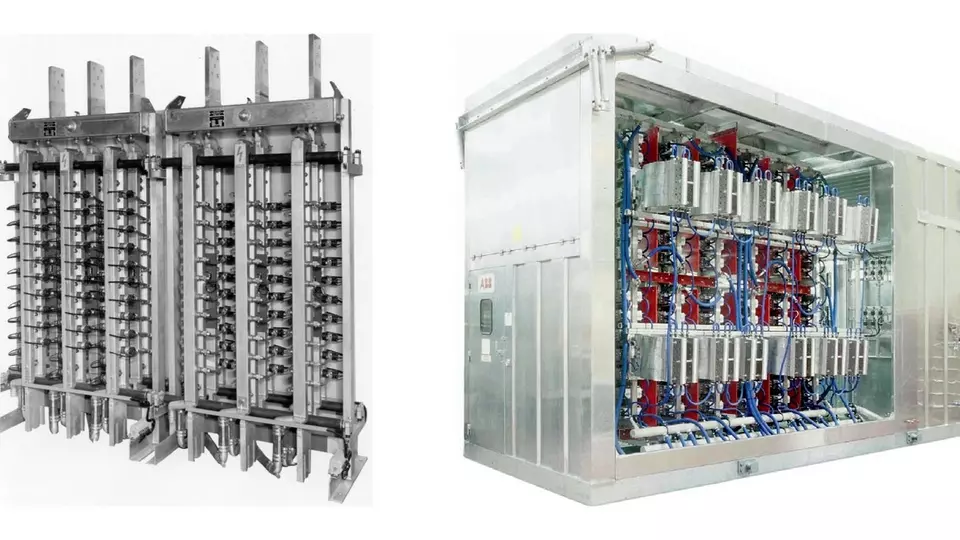
The global high-power rectifiers market is a critical component in the infrastructure backbone of power-intensive industries. These rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) at high voltage and current levels, serving applications such as aluminum smelting, chemical electrolysis, electric arc furnaces, and traction systems. As the world increasingly relies on stable and efficient power systems, the demand for high-power rectifiers continues to grow. However, the market faces numerous challenges that could hinder its growth trajectory. From high manufacturing costs and regulatory pressures to rapid technological shifts and supply chain disruptions, stakeholders must navigate a complex and evolving landscape.
1. Complex Manufacturing and High Initial Investments
One of the most significant challenges in the high-power rectifiers market is the complex manufacturing process, which demands precise engineering, custom design, and high-grade materials. These requirements contribute to elevated production costs, which can deter smaller manufacturers or new entrants. The capital investment needed for establishing facilities, testing labs, and obtaining certifications further increases the entry barrier. As a result, only a few major players dominate the market, potentially limiting innovation and competitive pricing.
In addition, the long development cycles and rigorous quality assurance processes necessary for high-reliability rectifiers, especially for defense and aerospace applications, slow down product deployment and increase the cost burden on suppliers and clients.
2. Fluctuating Raw Material Prices
High-power rectifiers heavily rely on critical raw materials such as copper, aluminum, silicon, and specialized insulators. Volatile prices for these materials affect production planning and profitability. Sudden price hikes, as witnessed during geopolitical conflicts or global supply chain disruptions, can make cost forecasting difficult. This volatility can delay large-scale infrastructure projects that depend on stable rectifier pricing.
Moreover, any shortage in semiconductor components due to global demand surges—like those experienced in the automotive and electronics industries—can delay production schedules and disrupt delivery timelines.
3. Stringent Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is another pressing issue. Manufacturers must align with multiple regional and international safety, energy efficiency, and environmental standards. With growing emphasis on eco-friendly technologies, there is increased pressure to reduce energy loss in rectifier systems and adopt recyclable materials in manufacturing. Meeting these requirements often demands re-engineering of existing product lines, re-certification, and increased R&D spending.
In addition, obtaining approvals from governing bodies such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) can be time-consuming and complicated, especially when targeting cross-border markets. Manufacturers need to allocate significant resources to ensure ongoing compliance while continuing to innovate.
4. Technological Obsolescence and Innovation Pressure
Technological advancements are reshaping the high-power rectifier industry. The emergence of digital control systems, power electronics based on silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), and smarter cooling mechanisms are pushing the industry forward. However, companies that fail to invest in these innovations risk falling behind.
For instance, many legacy systems are not compatible with smart grid networks or IoT-based monitoring, which are now becoming standard in industrial and utility applications. Upgrading old infrastructure or phasing out outdated products is both costly and logistically challenging, especially for large-scale systems embedded in industrial processes.
Moreover, the rapid evolution of technology has led to shorter product life cycles. To stay relevant, manufacturers must continuously innovate and improve efficiency, durability, and performance—all while keeping costs competitive.
5. Lack of Skilled Workforce
The specialized nature of high-power rectifier design and integration demands a highly skilled workforce. From electrical engineers to systems integration experts, the shortage of qualified personnel is a growing concern across many regions. As older engineers retire, companies are struggling to find new talent equipped with the knowledge and training required to manage high-voltage systems.
This skills gap delays development and increases reliance on a few seasoned experts, which in turn creates bottlenecks in production and maintenance processes. Companies must invest in training programs and collaborate with academic institutions to nurture a new generation of experts in this domain.
6. Global Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The COVID-19 pandemic revealed the fragility of global supply chains across various industries, and the high-power rectifier market was no exception. Shipping delays, factory shutdowns, and border restrictions affected the timely delivery of components and finished products. As companies reassess their supply chain strategies, many are considering localization and diversification to avoid future disruptions.
However, localizing supply chains involves significant restructuring and negotiation with local suppliers, which may not be immediately feasible, especially in regions with limited infrastructure or technical expertise.
7. Customization Demands from End-Users
High-power rectifiers are rarely one-size-fits-all. Industrial customers often request customized designs tailored to their unique operating environments, such as extreme temperatures, corrosive atmospheres, or specific voltage-current requirements. While customization adds value, it also adds layers of complexity to the design and production process.
Every custom order must go through an extended cycle of consultation, design, prototyping, and testing. This can significantly elongate project timelines and reduce throughput. Balancing the demand for customization with the need for standardized production remains a delicate challenge.
8. Geopolitical and Trade Tensions
In an increasingly globalized world, international trade policies have a substantial impact on the high-power rectifier market. Tariffs, export restrictions, and sanctions can limit access to crucial markets or critical components. For example, ongoing trade tensions between major economies can restrict the flow of semiconductors or force companies to seek alternative, often more expensive, suppliers.
These uncertainties affect long-term planning and can hinder partnerships between manufacturers and multinational clients. Companies must remain agile and develop strategies to mitigate geopolitical risks.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future Through Resilience
The high-power rectifiers market is pivotal to the functioning of numerous industrial sectors. While the demand is strong, the path forward is laden with challenges ranging from economic volatility and environmental regulations to technological transitions and labor shortages. Stakeholders who focus on innovation, flexible supply chains, talent development, and strategic partnerships will be better positioned to thrive.
Ultimately, turning these challenges into opportunities requires a proactive approach, visionary leadership, and sustained investment in cutting-edge technologies. As the world moves toward electrification and sustainable energy systems, overcoming these barriers will be essential in ensuring the high-power rectifier industry remains resilient and future-ready.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


