Soft Magnetic Material Market Impacting Factors: Investment in Smart Grid Infrastructure Boosting Use of Magnetic Components
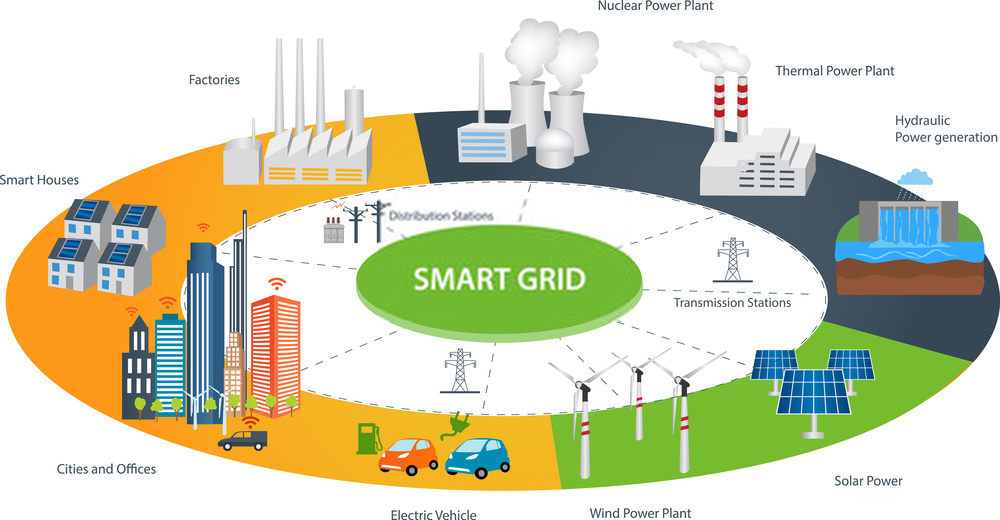
The global soft magnetic material market is rapidly evolving, shaped by multiple macroeconomic and technological forces. One of the most significant impacting factors today is the growing investment in smart grid infrastructure, which is dramatically boosting the demand for advanced magnetic components. As the energy sector moves toward digitization, decentralization, and decarbonization, soft magnetic materials have become indispensable in enabling the efficient transmission, transformation, and distribution of power across smart grids.
This article explores how smart grid expansion is reshaping the soft magnetic material market, the types of materials being used, and the strategic implications for manufacturers and stakeholders.
Understanding the Role of Soft Magnetic Materials
Soft magnetic materials, including silicon steel, ferrites, amorphous alloys, and nanocrystalline materials, are prized for their ability to magnetize and demagnetize with minimal energy loss. These materials are fundamental in designing inductors, transformers, sensors, converters, and electric motors—components that are essential in modern power systems.
As smart grids become more complex and interconnected, the need for high-efficiency, compact, and reliable magnetic components is increasing. The performance of these systems depends significantly on the quality and characteristics of the soft magnetic materials used.
Smart Grid Infrastructure: A Key Growth Driver
Smart grids are modernized power networks that use digital technology and automation to monitor, manage, and optimize energy flows. Unlike traditional grids, smart grids allow for real-time communication between utility providers and consumers, the integration of renewable energy sources, and efficient load balancing.
Governments and energy providers around the world are investing heavily in smart grid infrastructure to improve energy efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and increase grid reliability. This large-scale transformation is driving an increased need for magnetic components in:
-
Smart transformers
-
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI)
-
Power factor correction devices
-
Electric vehicle (EV) charging stations
-
Energy storage systems
Each of these systems relies on soft magnetic materials for optimal function, creating a positive feedback loop between smart grid investment and magnetic material demand.
Applications of Magnetic Components in Smart Grids
1. Smart Transformers
Smart transformers are critical in smart grid systems because they can regulate voltage, monitor power quality, and adapt to load conditions in real time. Soft magnetic materials, particularly amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys, are widely used in the cores of these transformers due to their high energy efficiency and reduced core losses.
These materials enable transformers to operate at higher frequencies and temperatures, increasing their durability and performance in dynamic grid environments.
2. Power Electronics and Converters
The integration of renewable energy sources—such as solar panels and wind turbines—requires efficient power conversion systems. Inverters and converters use soft magnetic inductors and transformers to convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), and vice versa.
With the rise of decentralized generation and two-way power flows, there is a growing demand for compact, high-frequency magnetic materials that support faster switching speeds and greater thermal stability.
3. Energy Storage Systems
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) are vital in stabilizing smart grids by balancing energy supply and demand. Magnetic components in these systems help regulate power delivery and ensure smooth charge and discharge cycles.
Advanced soft magnetic materials help improve energy efficiency and extend the lifespan of these systems by reducing power loss and heat generation.
4. Electric Vehicle (EV) Infrastructure
As EV adoption accelerates, smart grids must adapt to the increased demand for electricity. EV charging stations use magnetic components in their power supply units and voltage converters, making the role of soft magnetic materials even more crucial.
High-speed charging solutions, in particular, require magnetic materials that perform well at high frequencies, pushing manufacturers to develop new alloys and production methods.
Regional Investment Trends Supporting Market Growth
North America
The U.S. government has committed billions of dollars toward modernizing its aging grid through smart technologies. Projects funded under the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) and other green energy programs are boosting demand for smart grid components and, by extension, soft magnetic materials.
Europe
The EU’s Green Deal and "Fit for 55" initiatives are driving massive smart grid upgrades. Nations like Germany, France, and the Netherlands are actively integrating smart meters, renewable generation, and energy storage, leading to increased consumption of high-efficiency magnetic components.
Asia-Pacific
China, Japan, and South Korea are leading the smart grid transformation in Asia. China, in particular, is rapidly deploying smart substations and distributed energy resources (DERs), which require advanced magnetic materials. India’s nationwide smart metering and grid modernization plans are also opening new market opportunities.
Innovation and Competitive Landscape
The growing demand for soft magnetic components in smart grids is fostering innovation in both materials and manufacturing processes. Leading manufacturers are focusing on:
-
Nanocrystalline and amorphous cores for high-performance, low-loss energy transmission
-
Powder metallurgy to produce customized shapes and sizes for specific smart grid applications
-
3D magnetic component design for enhanced power density and miniaturization
As competition intensifies, companies that can offer materials with superior magnetic properties, thermal resistance, and mechanical durability are gaining an edge.
Strategic Outlook for Stakeholders
For stakeholders across the value chain—from raw material suppliers and magnetic component manufacturers to utilities and system integrators—the expansion of smart grid infrastructure represents a significant growth opportunity. To capitalize on this trend, companies must:
-
Invest in R&D to develop next-generation magnetic materials
-
Establish local and resilient supply chains to ensure timely delivery
-
Align with global energy efficiency and sustainability standards
Collaboration between energy providers and materials scientists will be key to developing scalable, cost-effective solutions that meet the evolving needs of smart grids.
Conclusion
As highlighted in this soft magnetic material market impacting factors analysis, the surge in investment in smart grid infrastructure is having a profound effect on the demand for magnetic components. With the power sector transitioning to a cleaner, smarter future, soft magnetic materials will continue to play a vital role in enabling advanced energy technologies. Industry players who adapt to these changes with agility and innovation are well-positioned to thrive in the years ahead.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


