Reasons for Peristaltic Pump Tube Rupture
Reasons for Peristaltic Pump Tube Rupture
Peristaltic pump tubing, as a consumable part of peristaltic pumps, may experience various types of damage during use. The reasons for peristaltic pump tube damage can include incorrect tube installation or the liquid having a certain corrosiveness, leading to premature or abnormal wear of the tubing.
Below, we will detail the reasons for peristaltic pump tube rupture:
The elasticity of the tubing itself is affected by two aspects: material issues and dimensional issues.
With the same wall thickness, the larger the inner diameter of the tubing, the worse the elasticity; conversely, the smaller the inner diameter, the better the elasticity. When the inner diameter is the same, the thicker the tubing wall, the better the elasticity; conversely, the thinner the wall, the worse the elasticity. In applications with high precision requirements, tubing of appropriate dimensions should be selected to reduce errors.
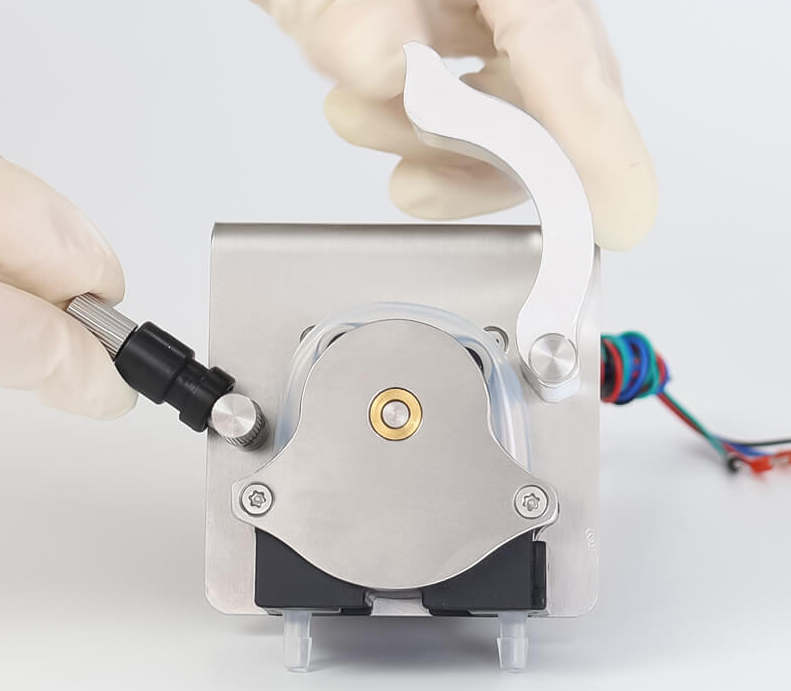
The dimensional accuracy of the pump is also one of the reasons for tubing rupture.
For the same piece of tubing, if the gap between the rollers and the arc is too small or uneven, the tubing will be subjected to localized excessive compression, leading to plastic deformation and affecting elasticity and transmission accuracy. Uneven pressure will also significantly shorten the lifespan of the tubing and increase the cost of using the peristaltic pump.
Changes in the liquid volume will also affect the condition of the tubing.
Changes in liquid volume can be summarized into two factors. The first is the temperature change of the conveyed liquid. Since the tubing is made of elastic plastic, different temperatures will change its elasticity. Generally, the higher the temperature, the worse the elasticity of the tubing; conversely, the lower the temperature, the better the elasticity. The second is the change in the position of the transmission liquid, which will affect the suction stroke of the peristaltic pump, thereby affecting the flow rate. The discharge head of the peristaltic pump has little effect on the flow rate, while the resistance at the suction side will counteract the rebound ability of the tubing, affecting the size of the rebound chamber.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


