Revolutionizing Renewable Energy: Waste to Energy Market Trends and Projections
Introduction
The Waste to Energy (WTE) Market plays a vital role in addressing global waste management challenges while simultaneously generating clean energy. With the rising concerns over landfill overflows and environmental pollution, WTE technologies have emerged as a sustainable solution. This blog explores the Waste to Energy market's dynamics, key drivers, challenges, trends, and future opportunities.
What is Waste to Energy?
Waste to Energy (WTE) refers to processes that convert non-recyclable waste materials into usable energy forms, such as electricity, heat, or biofuels. These processes help reduce landfill waste while contributing to global energy supply. The most common WTE technologies include:
-
Incineration: Controlled burning of waste to produce heat and electricity.
-
Gasification: Conversion of organic materials into synthetic gas (syngas) used for power generation.
-
Pyrolysis: Decomposing waste materials at high temperatures to produce bio-oil and synthetic gas.
-
Anaerobic Digestion: Using microorganisms to break down organic waste and generate biogas.
Key Market Drivers
-
Increasing Waste Generation
The global rise in municipal solid waste (MSW) due to urbanization and population growth is fueling demand for waste-to-energy solutions. -
Government Policies and Incentives
Many governments are implementing stringent waste management policies, tax incentives, and subsidies to promote WTE adoption. -
Growing Demand for Renewable Energy
The transition toward clean and renewable energy sources has boosted investments in WTE projects as an alternative to fossil fuels. -
Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
WTE processes help mitigate methane emissions from landfills, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Challenges Facing the Waste to Energy Market
-
High Capital Investment
Setting up WTE plants requires significant initial investment, which can be a barrier for developing nations. -
Technological Limitations
While advanced WTE technologies exist, some are still under development and require further improvements for efficiency and scalability. -
Public Perception and Opposition
Concerns over emissions from incineration plants and potential health risks have led to resistance in certain regions. -
Availability of Alternative Waste Management Solutions
Recycling and composting are often preferred due to their lower environmental impact, reducing the amount of waste available for WTE conversion.
More Information about the report:https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/waste-to-energy-market-wte/13394/
Emerging Trends in the Waste to Energy Market
-
Adoption of Advanced Gasification and Pyrolysis Technologies
New innovations in gasification and pyrolysis are enhancing energy output and minimizing environmental impacts. -
Integration with Smart Grids
WTE plants are increasingly being integrated with smart grid systems to enhance energy efficiency and grid stability. -
Expansion of Circular Economy Practices
Governments and industries are focusing on maximizing resource recovery from waste, promoting WTE as part of a circular economy strategy. -
Increased Private Sector Investments
Private companies are entering the market with new technologies and financial backing, accelerating market growth.
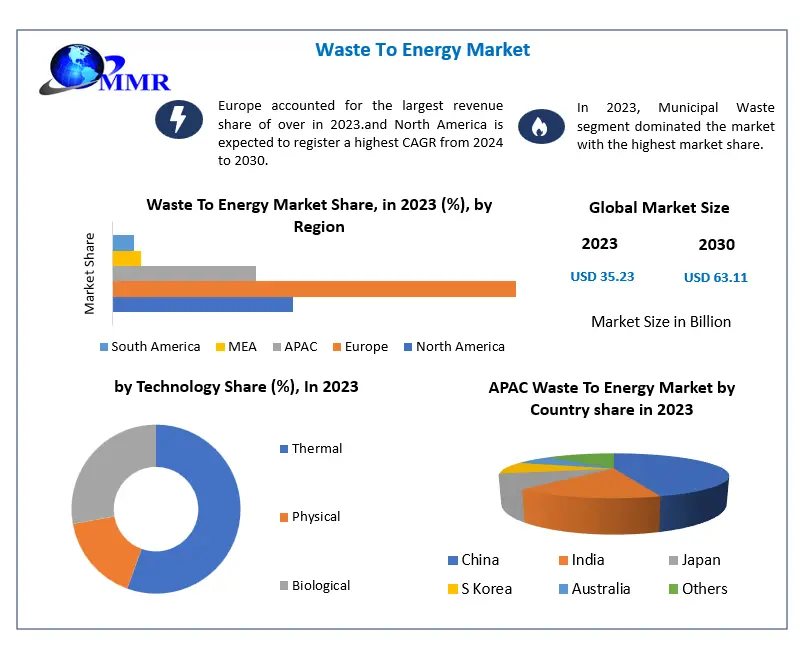
Regional Insights: Where is the Waste to Energy Market Thriving?
-
Europe: A leader in WTE adoption due to strict environmental regulations and ambitious sustainability goals.
-
North America: Increasing investments in WTE projects, particularly in the U.S. and Canada.
-
Asia-Pacific: Rapid urbanization and industrialization in China, India, and Japan are driving the WTE market's expansion.
-
Middle East & Africa: Emerging opportunities with governments exploring WTE as a solution to waste management issues.
Future Opportunities in the Waste to Energy Market
-
Developing Cost-Effective Technologies
Research and innovation in affordable WTE technologies can drive widespread adoption. -
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Collaborations between governments and private players can accelerate the development of WTE infrastructure. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Countries facing waste management crises present significant growth potential for WTE solutions.
Conclusion
The Waste to Energy Market is poised for significant growth as countries seek sustainable waste management solutions while addressing energy needs. With continuous advancements in technology, supportive regulations, and increasing environmental awareness, WTE stands as a key player in the transition to a greener future. Embracing these innovations will be crucial in mitigating climate change and achieving global sustainability goals.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Giochi
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Altre informazioni
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


