Magnesium Selenate Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025: Manufacturing Plant Setup and Operations
Introduction
Magnesium selenate is an inorganic compound primarily used in agricultural and industrial applications. It is a valuable source of both magnesium and selenium, two essential nutrients that play vital roles in plant and animal health. Magnesium selenate is commonly used as a fertilizer, providing both magnesium and selenium to plants, improving crop yields, and enhancing soil fertility. It is also used in animal feed, offering benefits for livestock growth and health. This Magnesium Selenate Manufacturing Plant Project Report presents an in-depth analysis of the process involved in setting up a manufacturing facility for magnesium selenate. The report covers the manufacturing process, raw materials, machinery requirements, market demand, financial considerations, and infrastructure needs for establishing a successful production unit.
Overview of Magnesium Selenate
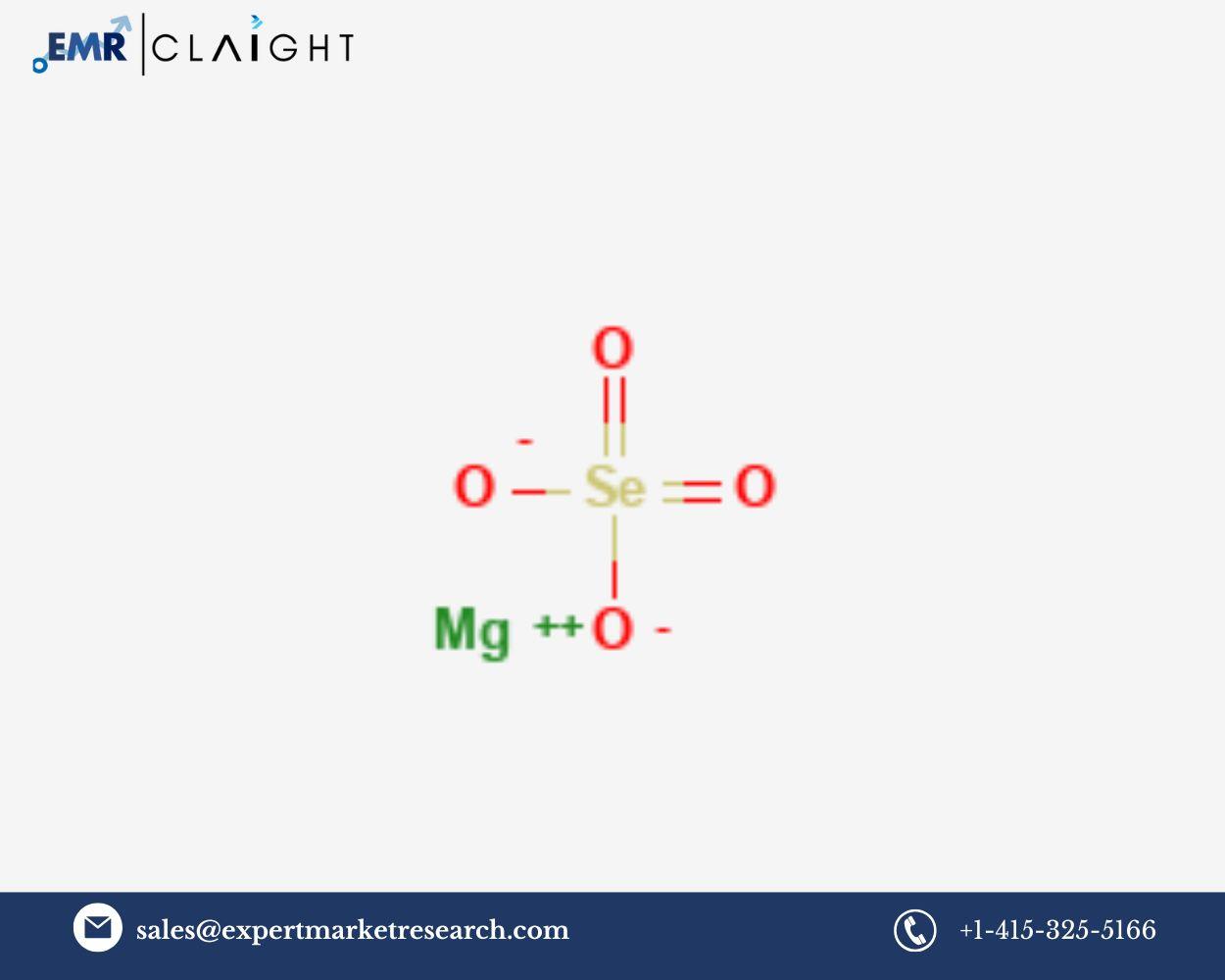
Magnesium selenate, with the chemical formula MgSeO₄, is a chemical compound that combines magnesium and selenium in a stable form. It is typically produced as a crystalline or powdered product, making it easy to use as a fertilizer or feed supplement. Magnesium plays a critical role in plant and animal metabolism, supporting enzyme functions, chlorophyll production, and photosynthesis. Selenium, on the other hand, is an essential trace element that helps protect cells from oxidative damage and is essential for the proper functioning of several enzymes and metabolic processes.
Key Features of Magnesium Selenate:
- Dual Nutrient: Provides both magnesium and selenium, making it a highly efficient fertilizer and feed supplement.
- Enhanced Crop Yields: Used in agriculture to improve plant health, enhance nutrient uptake, and increase resistance to diseases.
- Animal Feed Supplement: Added to livestock feed to promote growth, improve immune function, and prevent selenium deficiency.
- Environmental Impact: Magnesium selenate offers a more sustainable way to provide both magnesium and selenium to crops and animals, reducing the need for separate applications.
The growing demand for sustainable agricultural practices and the increasing awareness of the importance of trace elements in livestock health are driving the market for magnesium selenate.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Manufacturing Process of Magnesium Selenate
The process of manufacturing magnesium selenate typically involves the chemical reaction between magnesium salts and selenium compounds. The reaction is carefully controlled to ensure high purity and yield. Below is an outline of the general process involved in producing magnesium selenate.
1. Raw Material Preparation
The key raw materials required for producing magnesium selenate include:
- Magnesium Source: Magnesium sulfate (MgSO₄), magnesium chloride (MgCl₂), or other magnesium salts are commonly used as the source of magnesium.
- Selenium Source: Selenium dioxide (SeO₂) or sodium selenate (Na₂SeO₄) is used as the source of selenium.
- Water: Water is used to dissolve the raw materials and facilitate the chemical reaction.
2. Chemical Reaction
Magnesium selenate is produced through a reaction between magnesium salts and selenium-containing compounds. The typical reaction is as follows:.
3. Crystallization and Precipitation
After the chemical reaction, the magnesium selenate is separated from the solution by crystallization. The magnesium selenate crystals are allowed to form in a controlled environment, and then they are separated by filtration. The filtrate may contain sodium sulfate, which is removed to ensure the purity of the final product.
4. Washing and Purification
The crystallized magnesium selenate is washed with water to remove any remaining impurities or by-products. The washing process is critical to ensure that the final product is free from contaminants, such as sodium sulfate or unreacted raw materials. The purified magnesium selenate is then ready for the next stage.
5. Drying and Grinding
Once purified, the magnesium selenate crystals are dried to remove any moisture content. This is typically done using a rotary dryer or a vacuum drying system. After drying, the product is ground into a fine powder using grinding mills. This powdered form of magnesium selenate is ideal for use as a fertilizer or feed supplement.
6. Packaging
The final product is packaged in moisture-proof, airtight containers to protect it from contamination and preserve its shelf life. The packaging material is chosen to prevent exposure to environmental factors that could affect the quality of the magnesium selenate. The product is typically packed in bulk bags for industrial use or smaller packs for retail distribution.
Raw Materials and Inputs Required
The following are the primary raw materials and inputs required to set up a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant:
- Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO₄): The main source of magnesium in the manufacturing process.
- Sodium Selenate (Na₂SeO₄): The main source of selenium for the production of magnesium selenate.
- Water: Essential for dissolving the reactants and controlling the reaction environment.
- Energy: Electricity and thermal energy are required to maintain the reaction conditions and for drying the final product.
- Packaging Materials: Bulk bags, drums, and containers to package the final product.
- Labor: Skilled workers to operate the machinery, monitor the production process, and ensure quality control.
Machinery and Infrastructure Requirements
To set up a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant, the following machinery and infrastructure are required:
Machinery:
- Reactor Vessel: A large chemical reactor where the reaction between magnesium salts and selenium compounds takes place.
- Crystallization Tank: Used to allow magnesium selenate to crystallize and separate from the solution.
- Filtration Equipment: To separate the crystallized magnesium selenate from impurities.
- Washing Units: Used to wash and purify the magnesium selenate crystals.
- Drying Equipment: Rotary dryers or vacuum dryers to remove moisture from the product.
- Grinding Mills: To grind the dried magnesium selenate into a fine powder.
- Packaging Machines: For packing the final product in moisture-proof containers.
Infrastructure:
- Factory Building: A spacious and well-ventilated facility to house all production equipment and allow for smooth operations.
- Water Supply System: A reliable water supply for the production process and washing steps.
- Power Supply: A stable electricity source to power the machinery and maintain temperature controls.
- Storage Facilities: For storing raw materials, intermediates, and finished goods.
- Safety Equipment: Proper safety measures to handle chemicals, including protective gear, ventilation systems, and emergency equipment.
Financial Considerations
Initial Investment
The initial investment required to set up a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant includes the following:
- Land and Building: Cost of land acquisition and construction of the factory building.
- Machinery: Purchase of reactors, crystallization tanks, filtration equipment, dryers, grinding mills, and packaging machines.
- Raw Materials: Initial procurement of magnesium sulfate, sodium selenate, and water.
- Licensing and Permits: Fees for obtaining the necessary regulatory licenses and permits.
- Working Capital: Funds for labor, utilities, and raw material procurement.
Operating Costs
The operating costs for a magnesium selenate plant include:
- Raw Material Costs: Continuous purchase of magnesium sulfate, sodium selenate, and water.
- Labor Costs: Salaries for plant operators, technicians, and administrative staff.
- Energy Costs: Electricity and fuel costs for running production equipment and maintaining reaction temperatures.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance and servicing of machinery to ensure smooth operations.
- Packaging and Distribution Costs: Expenses related to packaging materials and transportation of the finished product.
Revenue Generation
Revenue from magnesium selenate production will come from the sale of the product to industries in agriculture, animal feed, and other sectors. The price of magnesium selenate depends on factors such as product purity, packaging, and market demand. Establishing long-term supply contracts with agricultural companies, livestock farms, and chemical producers will ensure steady revenue generation.
Market Analysis and Demand Forecast
The demand for magnesium selenate is driven by several factors:
- Agriculture: Magnesium selenate is used as a fertilizer to enhance crop yields, improve soil fertility, and provide essential nutrients to plants.
- Animal Feed: It is added to livestock feed to prevent selenium deficiency and promote growth and immunity.
- Sustainable Farming: The increasing trend towards sustainable and trace-element-based fertilizers is driving the demand for magnesium selenate.
- Global Food Production: As the global population grows, the demand for fertilizers and feed supplements is expected to rise, supporting the growth of the magnesium selenate market.
The market for magnesium selenate is expected to grow in the coming years, driven by the expansion of agricultural practices and the increasing need for high-quality animal feed.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Manufacturers of magnesium selenate must comply with various regulations to ensure product safety and quality. Key certifications include:
- ISO 9001: Quality management system certification to ensure consistent product quality.
- ISO 14001: Environmental management certification to minimize environmental impact.
- Fertilizer Regulations: Compliance with local and international standards for fertilizer production and distribution.
- Animal Feed Safety Standards: Adherence to safety standards for feed supplements to ensure the health and safety of animals.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporatio
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


